Australian Economy- Essay
1. Introduction
In this report we will discuss about the Education Industry reform in Australia. Australia’s higher learning has higher superiority and inclusive framework and is important on the planet. It pulled in numerous overseas understudies to complete their higher learning in Australia, for example, Chinese, Brazilian, or other understudies. Australian education industry could give higher superiority and world-perceived learning and proffer competitive lower educational cost expenses. Numerous students see the education structure suitable according to their needs. Hence, they find Australia as an education destination.
2. Comparative Analysis
Analyzing Education Industry of Australia with China
The market of Australia is well developed, and it obtains a higher degree on the internationalization stage of higher education. So an enormous piece of higher education understudies crosswise over national outskirts were foreign made into the English speaking countries, for example, “the USA, UK, Australia, Canada and New Zealand”. Australia acquires acclaimed “comprehensive research” colleges, and these remarkable staff of higher research performing colleges could draw in splendid understudies who dependably originated from wealthy families. These educational cost incomes can support its development, research ventures collaboration, rising aid to higher education.
The Chinese educational framework additionally got to be extension and expansion. Few “Chinese colleges” have being actualizing internationalization, for example, “Zhongshan University”, and it embraced global correspondence and trainings with overseas colleges. This alteration was influenced by government powers and market intercession. Contrasting with Australia, in Chinese higher education state apportionments and educational expenses are the major resources of income, which couldn’t satisfy its extension and coordinated improvement.
Another distinction is the private tertiary instruction amongst “China and Australia”. The type of learning privatization in China is autonomous privatization, and its private tertiary training incorporates the “People-Run” instruction and “People-Run Gong Zhu education”, which was generally unclear. However, the Australia educational part is well-developed; pulling in numerous overseas understudies to contemplate in Australia each year, however in Australia’s higher education still has separation on senior scholastic ladies. It is a drawback for Australia higher education to get a good scholarly surrounding and administration mode. Australia shows more prospects in a particular learning and teaching arrangement of a higher education contrasted with Chinese higher education. So to encourage the rapid global improvement of Chinese higher education, the legislature ought to bear on the higher education design reform, activate the eagerness of educators and understudies, and take review for the higher education coaching points and coaching rehearses (pyneonline.com.au, 2014).
3. GDP
Comparison of Australia with China
Australia
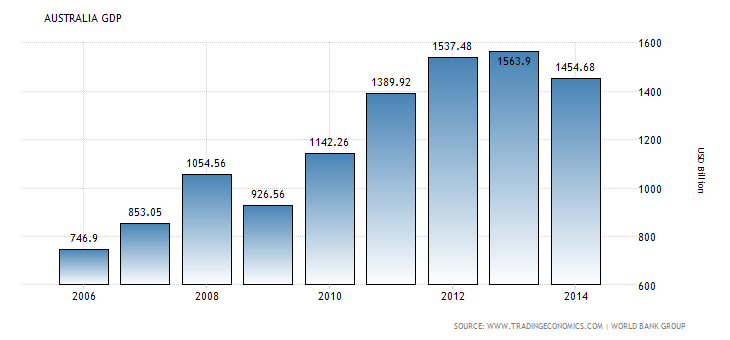
“Australia’s market is vanquished by its administrations division; however, its fiscal accomplishment depends on a lot of horticultural and mineral assets. Australia’s reputation in the export sector is fundamental indication of its natural wealth and domestic market. The country is a noteworthy nearby fiscal focus and an imperative constituent of the worldwide financial system.” (focus-economics.com, 2016)
China
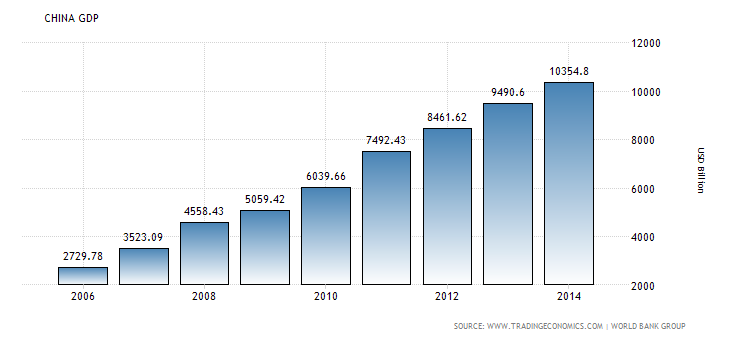
China has decided to set its GDP development target at 7.5% for the year 2014 and the similar was applicable in 2013. The country would like to keep the inflation percentage under 3.5%, however, the bad loan write-off, decline in spending over property and venture, other social reforms; hukou system and one child policy can affect the overall GDP growth of the country. (globalriskinsights.com, 2016).
4. Unemployment
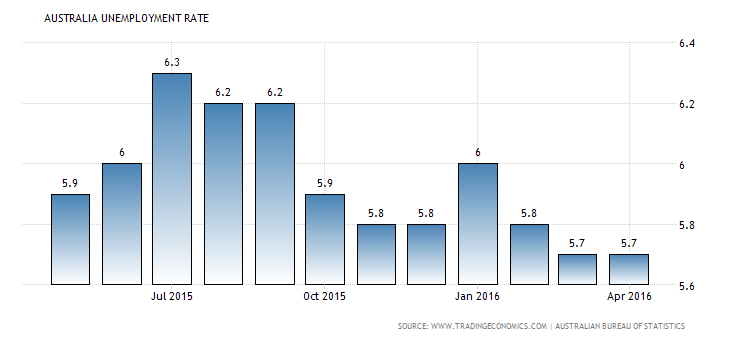
Rate of Unemployment in Australia
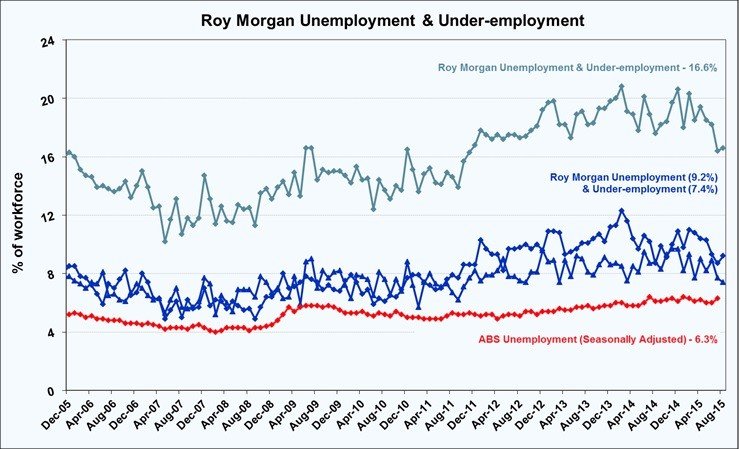
“Australia’s unemployment rate situated at 5.7% in 2016, unaffected from the number in March and somewhat below consensus of 5.8%. In Australia average unemployment rate was around 6.94% from 1978 to 2016, during this certain period of time, it was at peak with 11.10% in 1992 and the lowest with 4% in 2008”(theguardian.com, 2015)
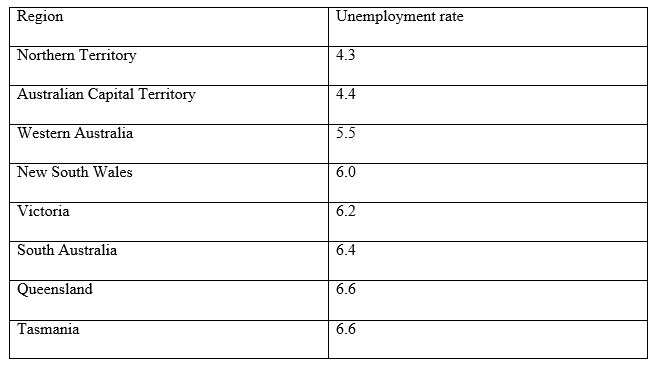
Unemployment rates by state and Territory, March 2015
Unemployment and Its types
There are 3 key and 4 major sorts of unemployment
The 3 main kinds are
- “Frictional employment: Fictional employment is a type of unemployment that occurs when an individual is jobless and seeking job in a healthy economy. In concise words, they will eventually go back to the labour forces. What differentiate frictional unemployment from other types of unemployment is that fact that it is an essential part of the normal labour turnover.
- Cyclical unemployment is the primary factor of the unemployment that is the consequences of the cyclical trends in the production that immerge during the business cycle. The decline in demand for products and services can eventually affect the demand graph to the point where less labor is required. As a result, the business will not have enough demand for labor which will slow down the production to a point where demand and supply are back in equalization”.
- Structural unemployment is the form of involuntary unemployment where an individual wants to work but could not do it due to a serious mismatch between what company seek and what employee can offer. Structural unemployment could be a significant issue inside a market, especially in situations where total parts (such as, manufacturing) get to be outdated” (boundless.com, 2016).
The 4 Major Sorts of Unemployment are;
- “Long-term unemployment arise when an individual search for job for more than 27 weeks or 6 months and more”.
- Seasonal unemployment is when a worker is unemployed due to the demand of a particular season. This sort of unemployment is common in specific industries that open for specific months of the year such as ice vendor, Christmas tree vendors, etc.
- Classical unemployment also known as “Real Wage Unemployment” arise when real wage increase above the marketing clear wage.
Issues
“Long-term unemployment ” is a growing issue for Australia, with around 600400 people in the country tolerating “Newstart Allowance for a year. The number is about to increase along with the worldwide budgetary crisis. “Long-term unemployment” of youngsters has additionally expanded quickly in Australia with just about 35% of adolescents are unemployed for over 12 months. This is a noteworthy issue as most estimates proposes that the general rate of joblessness would augment throughout the following couple of years, and youth joblessness builds more than proportionately. Numerous youngsters work in temporary and informal work, along with cyclically responsive organizations and eventually the first ones to lose their jobs in the economic downturn. The major problem occurs when unemployment is high and the margin is going up and youngsters who obviously have no idea about it sunk down deeper into the web and find it much difficult to discover another employment. Though there has been a noteworthy increment in the “preservation rate” of youngsters in schools and a major increment in youngsters moving on from colleges, they are as yet thinking that it’s tough to get work (smh.com.au, 2014).
Government Policy
The finance related procedure has long lasting impact on the financial development and administration. The political segments in the allotment of finances influence the unemployment rate. For example, ventures, for instance, “Streets to Recovery program’ amid the time of Australian election in 2001-04” has improved the monetary areas and reduced unemployment to some extent. The government constantly maintain budget balance through fiscal cycle, consider financial perils, national sparing adequacy, the cash related effects of approach decisions in future and the decency and relentlessness of the tax system with a particular end goal to achieve maintainable budgetary advancement which would diminish the unemployment. The governing body has set significance on the methodologies that raise the work control commitment. A part of the strategies is associated to the welfare with work bundle that has measures to lessen reliance on the welfare and development of motivating forces to go into the workforce. “Personal pay tax reductions with the minor duty rates cuts and extended edges, the Family tax cut changes have similarly extended the benefits to work. Hardly any measures are the late superannuation changes; work showcase changes to improve the work advertise flexibility to decrease basic joblessness, introduction of work showcase projects and preparing programs and the introduction of the “develop age laborer charge balance” have upgraded the work inspirations for the elderly people”. A couple of strategies are “microeconomic reforms” that upgrade asset assignment among business adventures and firms for generation augmentation that improve adequacy and productivity of creator. They are introduction of industry changes that give advancement that assemble yield and improvement by upgrading capability advancement and business creation; and tax collection changes. “The Council of Australian Governments had proclaimed the National Reform Agenda (NRA)” for the development of the labor force (business.unsw.edu.au, 2015).
5. Inflation
Comparing Australia’s inflation rate with China
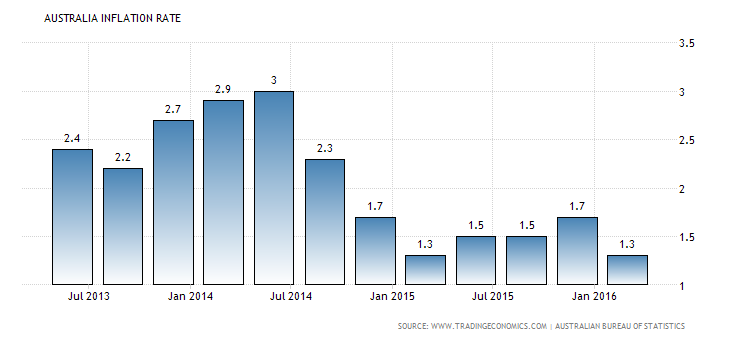
“Overall customer price in Australia has been increased 1.3% over the march quarter of 2016 from 1.7% in the previous quarter and under market agreement. This indicate that RBA trimmed mean CPI also increased to 1.7% in the first quarter of the 2016 abating from a 2.1% in the last quarter and under appraisals of a 2.0% ascent. Quarter-on-quarter, the list augmented went down from 0.2% to 0.6% in December.
RBA Weighted Mean CPI expanded to 1.4% year-on-year in the March quarter 2016, facilitating from 1.9%. Quarter-on-quarter, the list expanded 0.1& from 0.5%. For 2016, Australia’s national bank targets inflation from 02.0% to 3.0% on average basis. The quarter customer prices are also falling down by 0.2% closely following by 0.4% in December quarter. The average inflate rate in the Australia is 5.13% from 1951 to 2016. During this certain period of time, it reached to the record of 23.90% in the fourth quarter in 1951. Whereas the lowest rate -1.30% was recorded in the second quarter of 1962”. (tradingeconomics.com(b), 2016).
China Inflation Rate
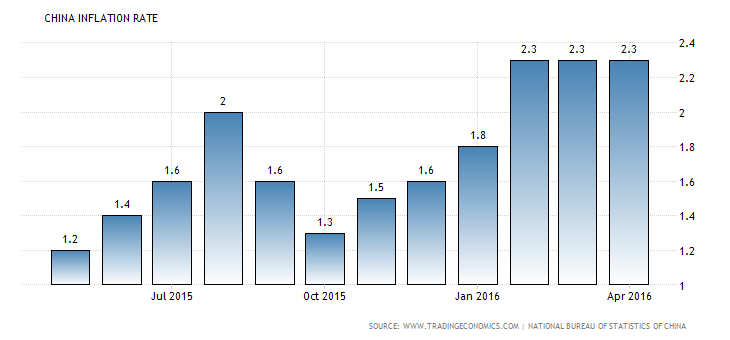
“In china client costs increased by 2.3% in year-on-year in April 2016, the comparative pace as mentioned in the last two months underneath the market accord of the 2.4% development. Politically sustenance costs extended by 7.4% when non-nourishment cost expanded with slower pace and reached 2.5% along with non-food cost at 1.1%. The expenditure on the customer merchandise eventually increased by 2.5% and administrations advanced by 2.0%. On the month to month premises, the shoppers cost has decreased by 0.2% when appeared differently in relation to a 0.4% abatement in the main month and as per assessment. Expansion Rate in China found the value of 5.49% from 1986 until 2016, accomplishing a recorded peak of 28.40% in February of 1989 and record lowest – 2.20% in April of 1999″ (tradingeconomics.com(c), 2016).
Inflation and Causes
Inflation means that there is a sustained increase in the price of the goods and services that are fundamentally caused by the deflation of money.
The Reasons for Inflation
Demand-pull inflation: In an economy demand-pull inflation appear in an economy when aggregate demand increase more rapidly than the production capacity of the economy The excessive push to the aggregate demand might come from the center bank that increases the flow of money in the economy.
Cost-push inflation: It occurs when the overall price of production increases. The increase in the cost of labor and raw materials are some of the main causes of such inflation. Main resources that can cause inflation in the Australia are oil price and salary factors. As salary frequently represents a noteworthy expense in business consumption, firms would endeavor to pass on a salary increment to purchasers in order to look after the profit.
Inflationary desires: If a customer desire an ascent in inflation, then they will respond in a way which will further expand the impacts of inflation. There are two fundamental ways how inflationary desires affects the level of inflation:
First: When the cost is predicated upon the rise, customers would buy before the expansion in costs. This will bring about an expansion in utilization bringing about higher demand-pull inflation Once the organization figures out the expansion for their products, they might anticipate the price of the product promoting the expansion in inflation.
Second: when workers expect the rise in the earning, they would consider it during the negotiation of the wage increment. Higher-wages during the inflation can further increase cost-push inflation.
Imported inflation: It is the form of inflation that occurs due to the increase in price of imports. As the import price increase, the domestic production that involves imported goods as a raw material also increases. The devaluation of Australian currency would prompt the residential cost of import which will automatically expand the level inflation.
Additional reasons are
- “Government approaches”; might either straightforwardly impact inflation through taxes.
- “Additional increments in monetary flow”; if the monetary flow in the economy exceeds the level of financial development, then an expanded volume of cash would be left pursuing the same measure of products and services along these lines expanding the level of inflation (Hall, 2009).
Government Policies to Sustain Low Inflation
Financial policy was the primary apparatus utilized by the “RBA” as a part of maintain the level of inflation, incidentally diverse approach blends are utilized to address price pressures in the market. Financial policies have been developed to support development at a level that doesn’t make exorbitant inflationary pressures. In the event that inflation starts to increase, the “RBA” would fix financial approach, in this way dampening customer and venture spending – bringing a lower increase in monetary development and thusly a lower level of inflation. Apart from this, “RBA” frequently utilizes pre-emptive financial policies, making a move to control the expansion before it becomes an issue. Monetary strategy has likewise assumed a part in keep up “low inflation” levels. In the event that the government utilizes” Contractionary financial strategy”, where it would expand income through tax collection and decline spending; the level of demand-pull inflation would diminish. Financial arrangement measures that bolster lower inflation levels might diminish or eliminate the requirement for sky-breaking interest rates to fight back and eventually resolve the inflation issue. The government has additionally executed “microeconomic strategies” in order to decrease the inflation level. Another assurance has brought down by the import costs. But at the other side strategies that are implemented to reduce the inflation brought the expansion in foreign rivalry, making it challenging for domestic makers to expand cost value of their products and services. “Reforms in the labor market” has been implemented to assure the expansions in earnings levels along with the efficiency. Governments have contended as of late that spending on infrastructure has diminished the limit limitations confronted by business that build production expenses and add to inflation (budget.gov.au, 2016).
6. Monetary Policy
“In February 2008 the RBA set its money rate at 7%, up by 25 basis points. Just a month later the RBA included another 25 basis points, with customer demand outpacing financial generation and in this way raising costs. Inflation now was at 6.5%, well over the objective rate. In 2008, the RBA lessened the money rate by 25 basis points. Short term ascents in the CPI were normal as oil costs were high, however in the long haul aggregate demand was adequately debilitated for inflation to fall prompting further cash rate decreases cumulating out a low of 3.00% in April 2009. The RBA set itself the objective of achieving target inflation by mid 2010. With Australia having weathered the monetary emergency exceptionally well, the RBA is beginning to raise interest rates once more. The cash rate at present stands at 4.25%. In the wake of having ignored to issue bonds with a perspective regulating money related supply, the Australian Office of Financial Management, arrangements to have issued treasury indexed bonds with an estimation of $150 billion by mid-2010, up from $6 billion only one year prior” (rba.gov.au, 2016).
The affects and issues facing by Australia are:
- “The neo-liberal mindset wins – fiscal austerity and a select dependence on money related policy to change general spending towards maintaining growth”.
- “Development is contracting and unemployment is increasing. This is because of a mix of components. Firstly, the end of the private speculation boom connected with mining boom. Secondly, cautious household utilization action as record levels of liability combining with rising joblessness. Thirdly, fiscal austerity – a refusal to utilize discretionary monetary approach towards counterbalance the decrease in private spending”.
- “The RBA has been lessening the money rate to condition lower interest rates all through the economy in a bid to encourage credit development to counter the decrease in spending and financial movement”.
- “Residential lodging costs, especially in Sydney are skyrocketting as lodging financial specialists are pricing owner-occupiers out of the business sector”.
- “The RBA expects that on the off chance that if the lowers interest rates further down to encourage total spending and stop the ascent in joblessness, it would exacerbate the speculative property action”.
7. Carbon Tax/ Emission Trading Scheme
Comparing Australia with China in ETS;
“Carbon markets”, proposed to influence polluters to dispense and diminish “emanations”, are more fundamental than some other time in ongoing memory. Nevertheless, the money related hang and the basic defects mean they’re reeling, another report proposes this.
China
The relieving news carbon exchanging world received this year was beginning of six regional top and-exchange plots in China. The country is known for producing 1,115 megatons of carbon dioxide into atmosphere through the plans, that makes China the second greatest carbon advertise on earth. Every one of the plans is insignificantly particular, with the carbon cost fluctuating between ¥20 ($3) and ¥80 ($13). China’s national government is failing to acknowledge which works most noteworthy before uncovering the country over program, possibly as in front of timetable as 2016 (theconversation.com, 2016).
Australia
Right opposing to China’s early accomplishment, a difference in government has seen Australia’s carbon advertise implode. Tony Abbott was selected as Australia’s pioneer in 2013 by and large environment skeptic stage. A highlight of his Liberal Party’s natural approach is to reduce Australia’s carbon duty and stop its masterminded coordination into the EU ETS. Or maybe, the organization needs to realize the need of “Immediate action plan” in which associations “agrees” to reduce emanations. The recommendation switches the emphasis of Australia’s discharges diminishment techniques to paying associations to control outflows, rather than exhausting their pollution (ipa.org.au, 2013).
8. Economic Growth
Comparing Australia with the Advanced Economy of China
Australia – GDP Data
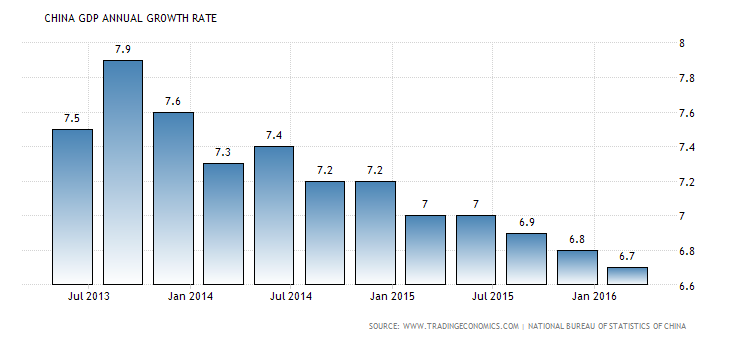
The economy of the China tried to push the development rate to “6.7% which was lower than previous year (6.8%) accordance with market demand. Economists consider it as the lowest development rate since the principal quarter of 2009. Long-term assets, resources, modern retail deals and Yuan credit actually expanded more than it was discussed in the March, proposing a quick rise in the economy. The GDP rate in China reached the mid-point of 9.85% for 1989 to 2016, to a record-breaking point of 15.40% in the first quarter of 1993 and the lowest3.80% at 1990. GDP annual growth rate was recorded by the National Bureau of Statistics of China.
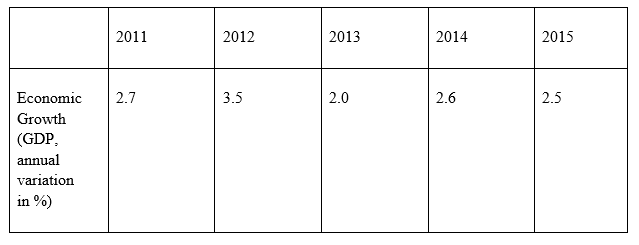
Right before the country faced the immense downturn from “1999 to 2008, Australia’s GDP reached 3.4%” on average for constant years. Economic growth rate diminished to “1.6% in 2009 as a delayed consequence of the worldwide budgetary turmoil. Despite the fact that 2009 was the most difficult year for the Australian economy after the downturn in “1991”, however, the economy presented a stunning adaptability to the overall crisis. In fact, Australia was one of the handful countries that recorded positive in “2009”. The financial performance has approved with “GDP development, averaging 2.7% from 2010 to 2013(focus-economics.com, 2016).
Quick financial ascendance has also expedited various difficulties, including higher discrepancy, speedy urbanization; challenges to environmental sustainability and external unpredictable characteristics. Australia moreover stands up to statistic weights related to a developing people and the interior development of work. Material expectations for everyday comforts are supported by money related improvement, exchange offs associated with monetary advancement, feasible budgetary improvement are sure positive effect on the general public.
The Chinese economy tried to enhance the annual “6.7%” in the imperative quarter of “2016”, that represented differently with 6.8% in the past year according to business division needs. Moreover, it was the lowest improvement since the quarter of 2009 settled asset venture, retail deals and new “yuan credits”, mechanical yield, all-inclusive more than analyzed in March recommending the economy is invigorating. Total annual growth in China found around the center estimation of “9.85% from 1989 until 2016”, achieving a record-breaking high of “15.40% up the essential quarter of 1993 and the lowest one 3.80% in the last quarter of 1990” (loc.gov, 2015).
9. Australian Budget May for 2014
Overall revenue for 2015-2016 is foreseen to be $405.4 billion, an increase of 5.5% on expected income in 2014 15. Total operating costs for 2015 16 are anticipated to be $434.5 billion, an augment of 3.4% on assessed operating expense in 2014 15.” are anticipated to be $434.5 billion, an enlarge of 3.4% on assessed operating expense in 2014 15.” (budget.gov.au, 2014)
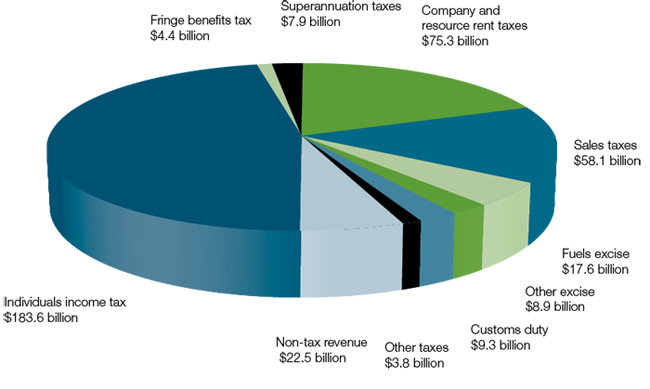
Where revenue comes from (2014‑15)
Where taxpayers’ money is spent (2014‑16)
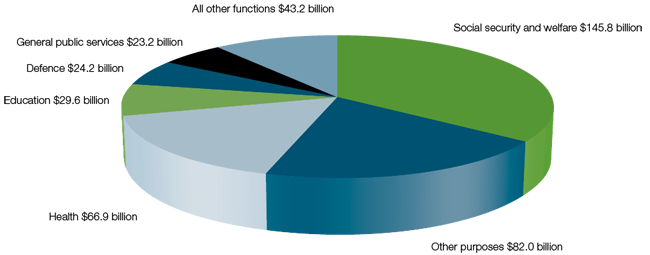
“Australia” pays lower taxes in comparison to other “OECD countries”. Regardless this, it has come to a period when government expenses have moreover been crossed, a pattern that is supposed to continue. Altering the financial budget could be practiced by concentrating on either income or expenses or both of them (budget.gov.au, 2014).
“The Federal Government’s National Commission of Audit” proposed that privileges, including some family favorable advantages should be rejected or better focused to lessen government spending. The commission did not break down the issue of income and charges, yet rather advocates keeping tax at the ” historical average of 24% of GDP” (budget.gov.au, 2014).
The comments were;
- By the social welfare groups stated that there’s an issue on both revenue and spending side – particularly the rate of development is an issue here.
- Another comments from a mining companies that even though enormous taxpayers because of the dimension of their operations, they were paying a much lower extent of their working profits as tax than whatever remains of the corporate segment, around 5 to 10% points less in accordance to “Treasury Secretary Martin Parkinson”.
- One comment by stakeholders that Australia’s focus on spending cuts makes balancing budget tricky
- You will have a hard time believing what they’re cutting … what’s more, spending … in the Federal Budget 2014, as stated by “Treasurer Joe Hockey”.
Source : (abc.net.au, 2014)
10. Conclusion
Thus from the above report we could conclude that Australia’s has a steady growth the educational industry but there is required few reforms for further flourishing of the industry.
References
abc.net.au, 2014. Does Australia have a revenue problem, as ACOSS chief executive Cassandra Goldie claims? [Online] Available at: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2014-05-08/does-australia-have-a-revenue-problem/5420474 [Accessed 31 May 2016].
boundless.com, 2016. Types of Unemployment: Frictional, Structural, Cyclical. [Online] Available at: https://www.boundless.com/economics/textbooks/boundless-economics-textbook/unemployment-22/introduction-to-unemployment-102/types-of-unemployment-frictional-structural-cyclical-390-12487/ [Accessed 31 May 2016].
budget.gov.au, 2014. Historical budget and net financial worth data. [Online] Available at: http://budget.gov.au/2014-15/content/overview/html/overview_36.htm [Accessed 31 May 2016].
budget.gov.au, 2016. Maintaining Low Inflation and Strong Growth. [Online] Available at: http://www.budget.gov.au/2000-01/papers/bp1/html/bs3-05.htm [Accessed 31 May 2016].
business.unsw.edu.au, 2015. Youth unemployment a major issue when economy takes a downturn. [Online] Available at: https://www.business.unsw.edu.au/news-events/news/youth-unemployment-a-major-issue-when-economy-takes-a-downturn [Accessed 31 May 2016].
focus-economics.com, 2016. GDP in Australia. [Online] Available at: https://www.focus-economics.com/country-indicator/australia/gdp [Accessed 31 May 2016].
globalriskinsights.com, 2016. 3 factors that will affect China’s GDP growth rate this year. [Online] Available at: http://globalriskinsights.com/2014/03/3-factors-that-will-affect-chinas-gdp-growth-rate-this-year/ [Accessed 31 May 2016].
Hall, R.E., 2009. Inflation: Causes and Effects. University of Chicago Press.
ipa.org.au, 2013. So now you have bought an emissions trading scheme. [Online] Available at: http://www.ipa.org.au/publications/1359/so-now-you-have-bought-an-emissions-trading-scheme [Accessed 31 May 2016].
loc.gov, 2015. The Chinese Economy. [Online] Available at: https://www.loc.gov/rr/business/asia/CentralAsia/china.html [Accessed 31 May 2016].
pyneonline.com.au, 2014. HIGHER EDUCATION REFORM SUMMIT: NEXT STEPS IN THE EVOLUTION OF AUSTRALIAN HIGHER EDUCATION. [Online] Available at: https://www.pyneonline.com.au/media-centre/speeches/higher-education-reform-summit-next-steps-in-the-evolution-of-australian-higher-education [Accessed 31 May 2016].
rba.gov.au, 2016. Monetary Policy. [Online] Available at: http://www.rba.gov.au/monetary-policy/ [Accessed 31 May 2016].
smh.com.au, 2014. Long-term unemployment in Australia doubles since the global financial crisis. [Online] Available at: http://www.smh.com.au/national/longterm-unemployment-in-australia-doubles-since-the-global-financial-crisis-20141010-113r2d.html [Accessed 31 May 2016].
theconversation.com, 2016. China announces national emissions trading scheme – experts react. [Online] Available at: http://theconversation.com/china-announces-national-emissions-trading-scheme-experts-react-48159 [Accessed 31 May 2016].
theguardian.com, 2015. Budget plan to limit unemployment benefits for under-30s scrapped. [Online] Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2015/may/12/budget-plan-to-limit-unemployment-benefits-for-under-30s-scrapped [Accessed 31 May 2016].
tradingeconomics.com(b), 2016. Australia Inflation Rate. [Online] Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/australia/inflation-cpi [Accessed 31 May 2016].
tradingeconomics.com(c), 2016. China Inflation Rate. [Online] Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/inflation-cpi [Accessed 31 May 2016].
tradingeconomics.com, 2016. China GDP Annual Growth Rate. [Online] Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/gdp-growth-annual [Accessed 31 May 2016].
Complicated microeconomics assignment help is another hurdle student have to face during their educational journey. From finding reliable sources to formatting and citing in a precise way, there are lots of tasks that are involved in an assignment writing task. In the hassle of the digital world, where excessive pressure has been put on the shoulders of students, Microeconomics assignment help service work as a much-needed saviour. Due to the lack of time and expertise, students often miss out the important details. Such problems can be easily resolved with the microeconomics assignment help provided by BookMyEssay.
The company has acquired the status of a leading academic writing service provider. They have a team of highly qualified, certified and skilled writers who have spent a decade writing assignments. Their expert team has a record of delivering every assignment before the deadline without compromising with the quality of the content. So, rather than wandering from website to website, students can rely upon the proficiency of the writers.
The professionals at website understand that assignment plays an important role in overall CGPA of students and hence, deliver the highest quality assignment to ensure students will receive the highest grades possible. They use simple language while writing, revise the content twice and run different plagiarism test to confirm its authenticity and uniqueness. Apart from this they pay attention to the personal growth of the students and cover the entire topic through their essay help, coursework assistance, and dissertation help.
In the past few years, the company has successfully expanded its customers’ networks across the globe covering major countries like the USA, UK, Australia, Hong Kong, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Jordan, Malaysia, etc. For the ease of the students, the company has also decided to create separate domains to target different continents. Feel free to visit the website to attain assignment help from the best Australian writers.


