Report to Metro Hospital Executive Boardon Roadmap to Achieving a HIMSS Level 7 EMR for the Metro Hospital by 2025
Health Informatics
Abstract
This is a business report which illustrates the strategies and timeframes in order to accomplish fully digital status of the Metro Hospital in Brisbane, Australia. The hospital has general surgical, midwifery, ENT, oncology, vascular, ophthalmology and other relevant general medical services. It also has number of health information systems and currently at EMR level 4. But the new Director of Informatics aims to implement level 7 of the HIMSS EMR Adoption model, which would further enable the hospital to attain fully electronic environment. This report explains a detail analysis and planning, strategy, timeframes, relevant technical factors while developing EHRs, its significance, resources, governance, associated benefits, risks, steps to overcome the identified risks and finally, provide with recommendations for the improvement of the care quality and stable maintenance of the implemented electronic care setup.
1. Background/Overview
This report presents a strategy to accomplish a particular goal set by the Health Informatics Division in Metro Hospital, Brisbane. The hospital aims to achieve level 7 HIMSS EMR Adoption Model by 2025. This report demonstrates how a health informatics professional could plan to achieve this.
The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) is a private organisation aims to develop the quality of the healthcare, improve cost-effectiveness, safety and better access through the best application of management systems and information technology (Connell and Young, 2007). The HIMSS level 7 indicates complete implementation of electronic medical record and data analytics to develop care.
Health Information Technology (HIT) illustrates wide-ranging health information management across computerised technologies. It describes about secure communication among the service consumers, service providers, quality entities, insurers, and the government (Brailer, 2010). The technology is gradually considered as one of the most proficient tool for developing general quality, safety and competence of the care set up and also service delivery. Broad and consistent application of HIT develops care quality and healthcare effectiveness, increases productivity, health care competence, prevents clinical errors, increases procedural correctness, care accuracy, reduces care costs, develops care work processes, administrative efficacies, reduces time on unproductive work, paper-work, accelerates communications on health informatics among healthcare personnel and develops access to low-cost care (Poulymenopoulou, Malamateniou and Vassilacopoulos, 2014). Inter-operative HIT develops the quality of individual patient care, brings diverse health benefits for public comprising early finding of the occurrences about infectious diseases around the state. It modifies tracking of disease management and evaluation of healthcare based on value facilitated by congregation of poorly identified quality information and price that can be judged against. It is an effective information processing application, which comprise both computer software and hardware in order to manage sharing, storage, retrieval, data application, information processing and knowledge associated with healthcare system for communication and decision making. Different forms of technology may include Computerized Physician Order Entry or CPOE, Electronic Medical Records or EMR, and Clinical Decision Support or CDS (Ebell, 2010). The substantial errors caused by handwritten notes, order entry, poor legibility and strange scientific abbreviations could be eliminated by the execution of health information technology (Harrington, 2013). The Metro Hospital presently has a number of health informatics systems and currently at EMR Level 4. This indicates the presence of electronic ordering that provides support in clinical decision making in medication and at least single area of clinical service. While information technology is gradually developing, it indicates a need to upgrade the healthcare system as well. Thereby, it is important for Metro hospital to achieve HIMSS level 7 by 2025.
HIMSS level 7 would enable the hospital to integrate complete EMR system in all the clinical areas, such as outpatient, ED and ICU and displace all the paper records in the setup. Data Warehouse would be used as the basis for the business and clinical analytics. Care continuity standard would be maintained while exchanging data (Sittig, Gonzalez and Singh, 2014). Thus, this report will demonstrate how a health informatics professional could achieve the level 7 of HIMSS EMR Adoption Model by 2025, with the help of comprehensive planning in the Metro hospital.
2. Vision for the EMR
The Metro Hospital has various numbers of health information systems and is currently at EMR Level 4. As a health informatics professional the vision of the writer is to achieve level 7 of the HIMSS EMR Adoption Model by 2025 and enable the hospital to work in a fully electronic environment. The services comprise general medical, surgical, vascular, ENT, oncology, ophthalmology, and palliative care and midwifery services.
The hospital will implement complete EMR in all the clinical areas, by displacing medical paper records within the hospital, and maintain care continuity standards. The system will comprise document management system, data mart, analysis, report making, and biometric implementation.
The steps of integration would include assessing practice readiness, planning approach, certified upgradation, conducting training, accomplish meaningful use, constant quality improvement. An assessment would be carried out based on current practice, goals, financial, technical readiness and needs. Based on the level of preparedness the entire practice could be designed so than plan could be implemented to meet the specific practice needs (Belletti, 2010). Planning would employ gathered information during evaluation phase to outline EMR implementation practices. Selection of right EMR is highly necessary for the practice. Effective hospitals and competent care professionals require to execute efficient technology to accomplish meaningful use and meet the requirements for incentive payments. The execution involve EMR system installation and related activities like pilot testing, training and so on. The final stage of implementation would include successful verification to demonstrate meaningful application of the EMR and further evaluation of what is learnt from the training and regular system application. The care professionals need to continuously focus on practice goals, post-EMR implementation in order to improve workflow and accomplish practice goals, while influencing the functionality of EMRs (He and Yan, 2014). The critical success factors for the EMR includes selecting right leadership team, proper communication of what is the actual transformation, analysing present workflow, creating measurable and specific goals, developing strategy for incorporating existing data, sufficient training time, creating power users, creating effective plan for solving problems and so on.
3. Analysing the Current Situation
The health services of the hospital respects patients’ privacy. ‘The Viewer’ is a web-based application, which sources electronic information from various systems. It is available to individual health departments, community centres, primary care setup and outpatient centres. It has been identified that some patients want to use another name while receiving health related services. This sometime prevent the hospital professionals to find relevant information the hospital already had in their record and provide with appropriate care. Biometric system would help in searching records, match and merge records of the patients who are unwilling to reveal their names. This indicates a need to review of the existence of biometric system, ‘data marting’ system and existence of patient portal system (Achampong, 2014).
To assess the current status of health informatics in the Metro hospital, it is important for the health informatics professional to estimate and control if the budget of meeting EMR is worth and the whether the hospital would make good profit by implementing EMR system. For instance: the professional needs to determine if the needs in the 1st stage would exceed the price of incentive check and evaluate the costs, which would have to be generated by meeting all the 7 stages after these pass auditing. One need to review if the EMRs meet the application justifiably and determine the time frames (Harrington, 2015).
Besides, the current status of the Metro hospital needs to be evaluated, which would include understanding of the aim of the hospital, its component deployment, corporate goals and its short-term needs. It is evident that the hospital is presently maintaining good associations with the local Division General Practitioners but they are not linked electronically. Hence, a system could be introduced where these physicians could be interconnected electronically along with establish a link between the electronic records of the hospitals. Application of manual process could delay the initiation of individual patient care within the hospital. This indicates a need to review manual process of searching records and replacing those with electronic health records that saves time, and financial investments on such activities. The amount of time spend to attend individual patients at Metro hospital and the effectiveness of the implementation of EMRs on reducing the time per patients will be another important aspect that needs to be reviewed.
4. Aspects Critical to Supporting an EMR
Adequate technical support is important factor to counteract conflict of applying electronic medical records. The characteristic of technical support includes IT helpdesk, training and so on. The consistent hospital-wide helpdesk could be required for all sorts of IT problems along with issues in electronic medical records. The hospital needs to ensure that the certified professional demonstrates what the system can perform during the training and subsequently us the system and application of regular helpdesk. Technical factors influence the execution of electronic medical records. It comprises belief of the presence of technical infrastructure, which support the application of the system. In this regard, mentioning of Roger’s diffusion theory is of highly necessary as it is related to the observability and ‘triability’ of an innovation (Rogers, 2003).
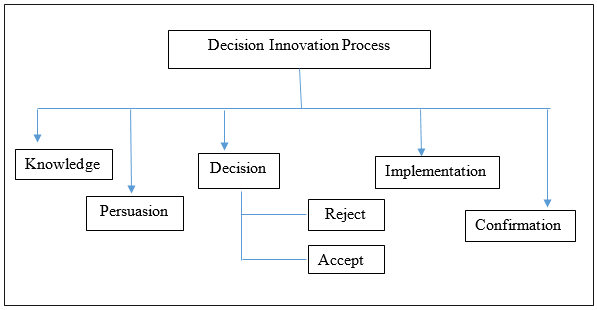
Fully digital healthcare technology and information management system coverage to develop digitised healthcare system. It is believed that convergence would move the concentration of healthcare digitisation to an incorporated eco-system, which reduce healthcare associated costs through analytics. Fully digitalised healthcare system would include digitising clinical back-office, digitising clinical front and back office activities, integration and monetisation.
Presently, EMR products are supported with various standards in terms of both development and product design. Major focus needs to be placed on developing EMR design. To diminish the design error and other associate consequences, certain changes are approved, regulated and monitored. Federal regulations need to be broadcasted which establish monitoring and approval process and the standards of the EMR systems along with implementation specifications. Federal regulations need to mandate that the EMR system developers use design, standards which optimise system efficacy, safety along with information integrity. The systems need not be marketed without approval and scrutinising. An industry standard needs to be in place for EMR design, quality principles (Faullant, Fuller and Matzler, 2012). The developers need to adopt processes and principles. Industry standard need to make sure about comprehensive quality management processes and principles that are adopted throughout the EMR industry in order to provide assurance in which case the EMR products could meet the minimum reliability, usability and safety. This indicates that information management practices need to be implemented to ensure its effectiveness.
5. Roadmap for Achieving HIMSS Level 7 by 2025
Implementation of HIMSS level 7 is a series of process thereby comprise of barriers, solutions and impact on clinical processes.
Some major goals to achieve full digitalise status for the hospital would include planning for EMRs and attainment of ambulatory EHRs. Hence, intake process, evaluation and medication process would be clearly evaluated. Clinical documentation and support would follow through e-communication patient portals and patient providers. The final stage of execution of EMR system would be make legalised by 2025. Thus, the health informatics professional aims to achieve fully electronic status by the year 2025. There is a need to use information technology and automation to develop the care provision for the patients.
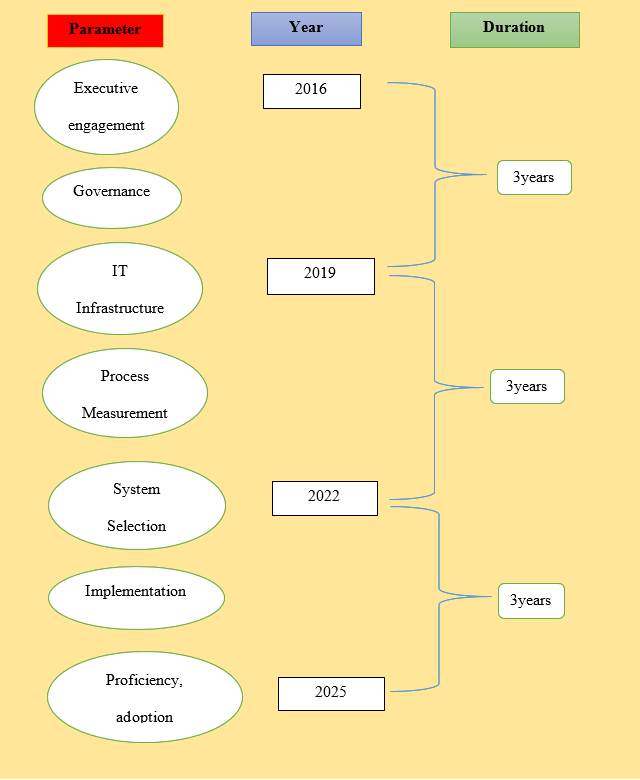
Developing specific goals and timelines to achieve a ‘fully digital’ status by 2025.
To achieve specific timelines and goal for the accomplishment of fully digital status for the hospital by the year 2025, a strategic plan, consensus and vision need to be develop at the executive or board level that would aim to transform the delivery of care through various business initiatives. A governance structure needs to be developed to facilitate accountability, decision making, management and prioritisation that comprise user-focused comprehensive plan and informs individuals to deal with transformation. After the process, a firm information technology which supports EMRs along with a business recovery continuity plan for the hospital needs to be in place (Wang and Biedermann, 2013). Technologies need to be executed where suppliers’ decision also need to be considered in an appropriate way. Technology related change management, achievements and measurements need to be maintained in regular work. Governance structure also needs to be in place to simplify management, accountability, and prioritisation along with decision making that comprises comprehensive functional piloting committee. For this hospital, measuring business processes needs to be extended along with the goals and balanced to initiate long journey of accomplishing level 7 by 2025.
6. Implementation Plan
Planning have a purpose, management overview, system overview that would include implementation description, point of contact, implementation schedule, major works, privacy, security, system security features and security setup during implementation of process. Besides, execution plans would make up of hardware, software facilities, materials, professionals and documentation. Professionals would undergo necessary training for staff implementation and further requirements. Planning would also include performance monitoring, execution of impact along with configuration management interface. Finally, the implementation would make up of implementing needs based on the location requirement details (Haughom, 2011).
Certain resources which are required to execute EMR project would include execution of certain technologies like Team Viewer, Skype that are used to offer remote access from home and office though application of wireless support, qualified professionals, who are well aware of these technologies and would not act as a barrier in implementing change within the hospital, physical resources as laptops, desktops, other gadgets, table, chairs and so on. Proper financial allocation of different departmental and administered funds needs to be highlighted (Zeng, 2016). During implementation of the plan, determining relevant resources would help the professional to predict possible threats, overspending, underspending and thereby, effectively monitor entire expenditure. As a whole, required resources could be non-financial and financial as well.
7. Governance
How will you govern your project? Governance is one of the most important factor in the present planning, as vague plans could pose great risk for the hospital in terms of HIMSS EMR Adoption Model by 2025. Relevant committees and their responsibilities need to be clarified in an appropriate way during the planning implementation. The committees for the Metro hospital could be clinical committee and IT committee (Han, 2014). These departments would oversee HIMSS level 7 implementation. Professionals who will be involved in dealing with different execution process need to establish good rapport with one another as working together to achieve the shared organisational goal is one of their major responsibilities. The professionals need to maintain dignity while working together within the group. Rules and regulations for making decisions needs to be maintained throughout the project and governance arrangement would include responsibilities of the agencies and reporting to responsible committees or the agency boards within the Metro hospital. The entire project needs to be governed in a way so that it comprise all the necessary services which are supposed to be offered as a consequence of implementing EMRs (Shaw, 2006). All the care professionals need to carry out need analysis to ensure that the implemented EMR system will act as guide for proper decision making for caregivers. Separate governing bodies of the hospital needs to work in a collaborative manner so that the plan get implemented in an appropriate way. The committees need arrange meetings at appropriate intervals in order to discuss emergency issues and solve those issues as early as possible in order to avoid any unwanted situation.
8. Alignment to State and National eHealth Programs
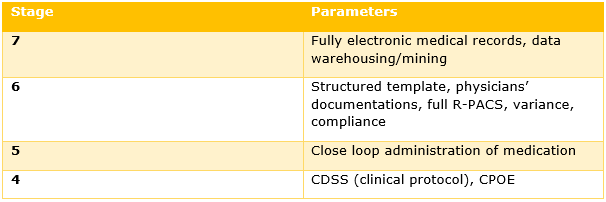
During the 4th stage, the Computerised Practitioner Order Entry (CPOE) that was used by the clinicians of the Metro hospital would be added to the data storehouse and nursing setup along with the potential of the decision support by the professionals which are associated with medicine based protocols. The accomplishment of prior stages indicates accomplishment of the 4th stage. Next stage would include incorporation of ‘close loop administration’ in any care service department and execution of the eMAR, bar coding and other relevant technologies that are applied in automated identification to increase safety, point of care, especially applied in medication administration, such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) (Klöcker, Bernnat and Veit, 2015). Next stage would comprise complete documentation of physicians’ documentation in one of the patient care service department. All the care professionals will be guided through these levels that would support them in making clinical decision associated with protocols and consequences in terms of modification alerts and compliance. In the radiology department, all the film based copies will be replaced by Picture Archiving Communication System that would provide the care professionals with clear images via intranet.
9. Likelihood of Success and Identification of Risk
Proper planning prior execution would enable the professional to accomplish the goal of incorporating HIMSS EMR level 7 in the Metro hospital. Nevertheless, there is a concern if certain practitioners of this hospital struggle to enhance their skills in accordance with upgraded technologies, quality reporting that involve meaningful execution of health related information technology. Other risks may include inadequate policy awareness, technology misuse and so on. High data security needs to be in place or else there is a high change of disclosure of internal records via despoilment of websites, social engineering, mail phishing, which are detrimental for the Metro hospital. This indicates a need to focus more on disaster recovery plans and various policies related with response recovery (Fritz, Tilahun and Dugas, 2015). Application of benchmark metrics is important as it helps in providing usability ratings, which could be developed via estimating actual clinical setup. Subsequently, a panel would compare effective performance against the perceive performances by the service users that would further establish a target score and better reflect the needs and demands of the service users. This would be more effective than the existing simple EMR performances (Tillett, 2012).
10. Conclusions/Recommendations
For successful implementation of the HIMSS EMR level 7 Adoption model in the Metro hospital, the health informatics professional needs to take care of the benefits, risks and implementation barriers, prompt acknowledgements of which could help the professional to achieve a bigger success. The change from manual operation to entirely EMRs is a noteworthy transition in the health care practice in the Metro hospital. Such transition would provide the hospital with further opportunities to initiate practice alteration and improve quality of care. In case of any inhibition is identified among the care professionals regarding the implementation of change, proper communication and training support need to be structured. The success will majorly depend upon various inputs provided by various departments. Quality improvement increase the productivity of the hospital and thereby profitability. The committees should strictly deal with governance in terms of project execution and through them the stakeholders would provide advice and suggestions, incorporation of these suggestions in decision making is highly beneficial. Relevant technicalities need to be considered in the context of EMR implementation, which would also ensure about improved healthcare and inform compliance with regulatory practices.
Appendix
References
Achampong, E. (2014). Electronic Health Record (EHR) and Cloud Security: The Current Issues. IJ-CLOSER, 2(6).
Belletti, D. (2010). Perspectives on electronic medical records adoption: electronic medical records (EMR) in outcomes research. Patient Related Outcome Measures, p.29.
Brailer, D. (2010). Guiding The Health Information Technology Agenda. Health Affairs, 29(4), pp.586-595.
Connell, N. and Young, T. (2007). Evaluating healthcare information systems through an “enterprise” perspective. Information & Management, 44(4), pp.433-440.
Ebell, M. (2010). AHRQ White Paper: Use of Clinical Decision Rules for Point-of-Care Decision Support. Medical Decision Making, 30(6), pp.712-721.
Faullant, R., Fuller, J. and Matzler, K. (2012). Mobile Audience Interaction – Explaining the Adoption of New Mobile Service Applications in Socially Enriched Environments. Engineering Management Research, 1(1).
Fritz, F., Tilahun, B. and Dugas, M. (2015). Success criteria for electronic medical record implementations in low-resource settings: a systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 22(2), pp.479-488.
Han, Q. (2014). Design and Application of Electronic Medical Record Template. Chinese Medical Record English Edition, 2(2), pp.41-46.
Harrington, L. (2013). Making Health Information Technology Usable. Health Affairs, 32(3), pp.629-629.
Harrington, L. (2015). Can Health Care Survive Current Electronic Health Record Usability?. AACN Advanced Critical Care, 26(3), pp.194-196.
Haughom, J. (2011). Implementation of an electronic health record. BMJ, 343(sep27 2), pp.d5887-d5887.
He, H. and Yan, Y. (2014). Design of Hospital EMR Management System. IJUNESST, 7(5), pp.341-348.
Klöcker, P., Bernnat, R. and Veit, D. (2015). Stakeholder behavior in national eHealth implementation programs. Health Policy and Technology, 4(2), pp.113-120.
Poulymenopoulou, M., Malamateniou, F. and Vassilacopoulos, G. (2014). Document Management Mechanism for Holistic Emergency Healthcare. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics, 9(2), pp.1-15.
Rogers, E. (2003). Diffusion of innovations. New York: Free Press.
Sittig, D., Gonzalez, D. and Singh, H. (2014). Contingency planning for electronic health record-based care continuity: A survey of recommended practices. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 83(11), pp.797-804.
T. Shaw, N. (2006). Clinical Governance and Laboratory Medicine: is the Electronic Medical Record our best friend or sworn enemy?. Clinical Chemical Laboratory Medicine, 44(6).
Tillett, J. (2012). Implementing the Electronic Medical Record. The Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing, 26(4), pp.284-285.
Wang, T. and Biedermann, S. (2013). Solve the Puzzle of Electronic Health Record Implementation Budgeting. The Health Care Manager, 32(1), pp.43-48.
Zeng, X. (2016). The Impacts of Electronic Health Record Implementation on the Health Care Workforce. North Carolina Medical Journal, 77(2), pp.112-114.
Writing the report on the nursing and medical science is no child’s play as subjects are complicated in nature and require proper knowledge to write upon. Students pursuing the degree in nursing need to know that there are numerous hospital working moving ahead with the aim to achieve HIMSS stage 7 which will help them understand its organization that improving technology and process can lead toward better patient care. BookMyEssay offers nursing assignment help to students to get a better understanding of HIMSS stage 7.
The team working at the website is globally known for providing reliable academic assignment writing help to students around the world. They have a flair of writing along with the dedication of delivering the content before the deadline. Writers working at the site stay stick to the university standards and norm while drafting an assignment or business report writing. They take pride in delivering a wide range of writing services for more than 100 subjects including engineering, medical science, biology, mathematics, law and more. Along with the quality content, the website also provides a list of references at free of cost.
Another advantage of working with BookMyEssay is their services come at the cost which will easily fit in student’s pocket. No matter how cryptic or complicated the assignment is, professional writers can handle it brilliantly. With 24*7 student support service, they are the ideal partner for your business report writing. To know more about services visit bookmyessay.com today!


